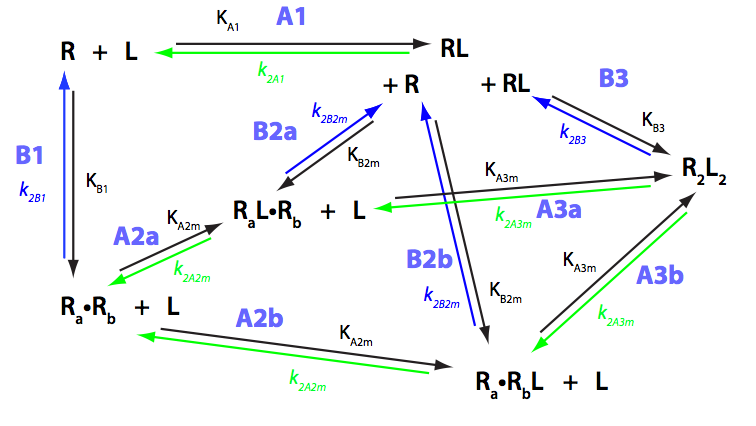

Discussion of relationships of the macroscopic and microscopic binding and kinetic constants is presented in tutorial_B. Definitions and relationships between the constants in the current model may be found in B_R2_R2L2.pdf.
Here, inherent symmetry of the binding sites in the dimer allows us to simplify treatment because the binding and kinetic constants are identical for the sites. However, microscopic treatment is still required to obtain insight into cooperation between the sites.
NOTE:
I only have time to test whether the model is operational. I plan to do detailed study of its behavior it in the future. Meanwhile, you may test different cases yourself as I did for other models.
Simulate setup_implementation_test B_R2_R2L2_test1
report: summary_report
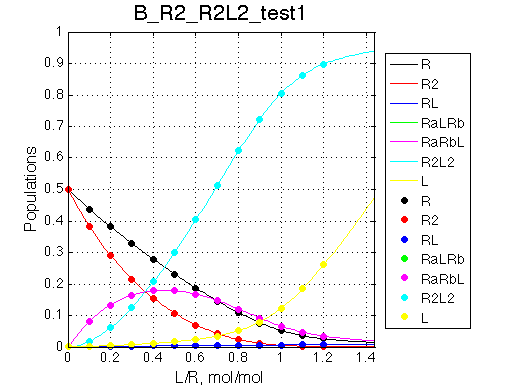
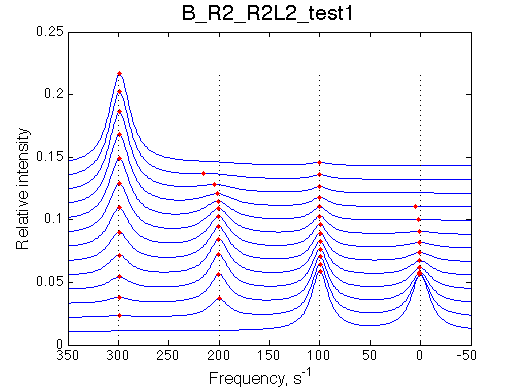
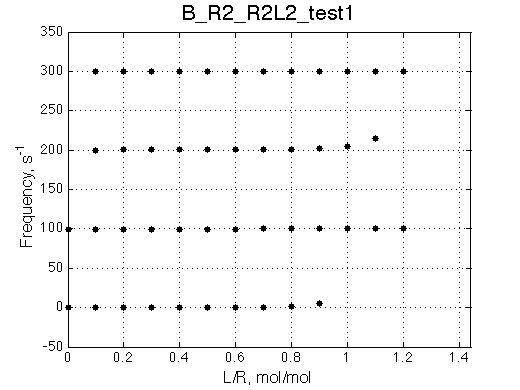
Seems working.
Here I bring the model into the fast binding/intermediate isomerization mode causing narrowing of the peak as it crosses the chemical shift of the non-binding species R.
Simulate setup_implementation_test B_R2_R2L2_test2
report: summary_report
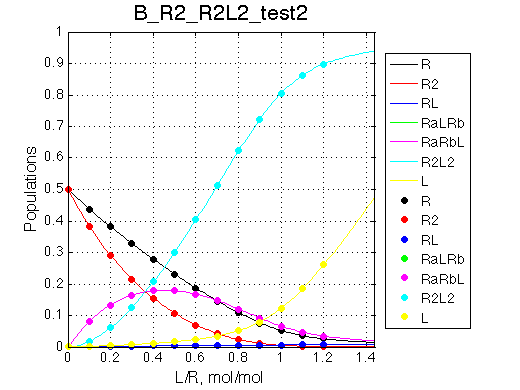
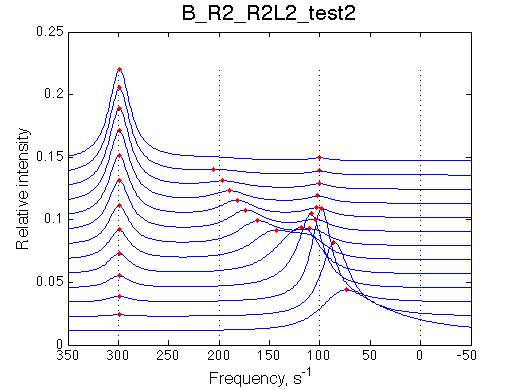
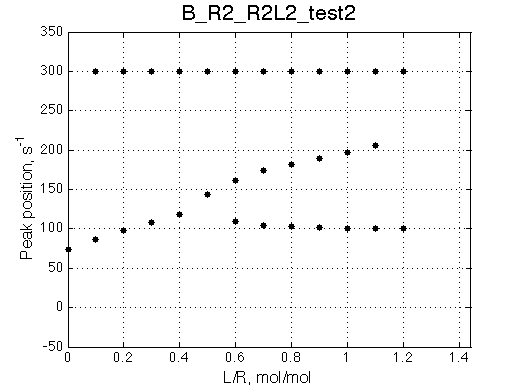
Peculiar phenomenon is observed here as well as in other models under conditions of fast exchange peak crossing resonance position of non-binding form of the receptor.
The model seems working.
Back to LineShapeKin Simulation Tutorial